New paper on the analysis of isomeric homo and copolymers by ion mobility mass spectrometry
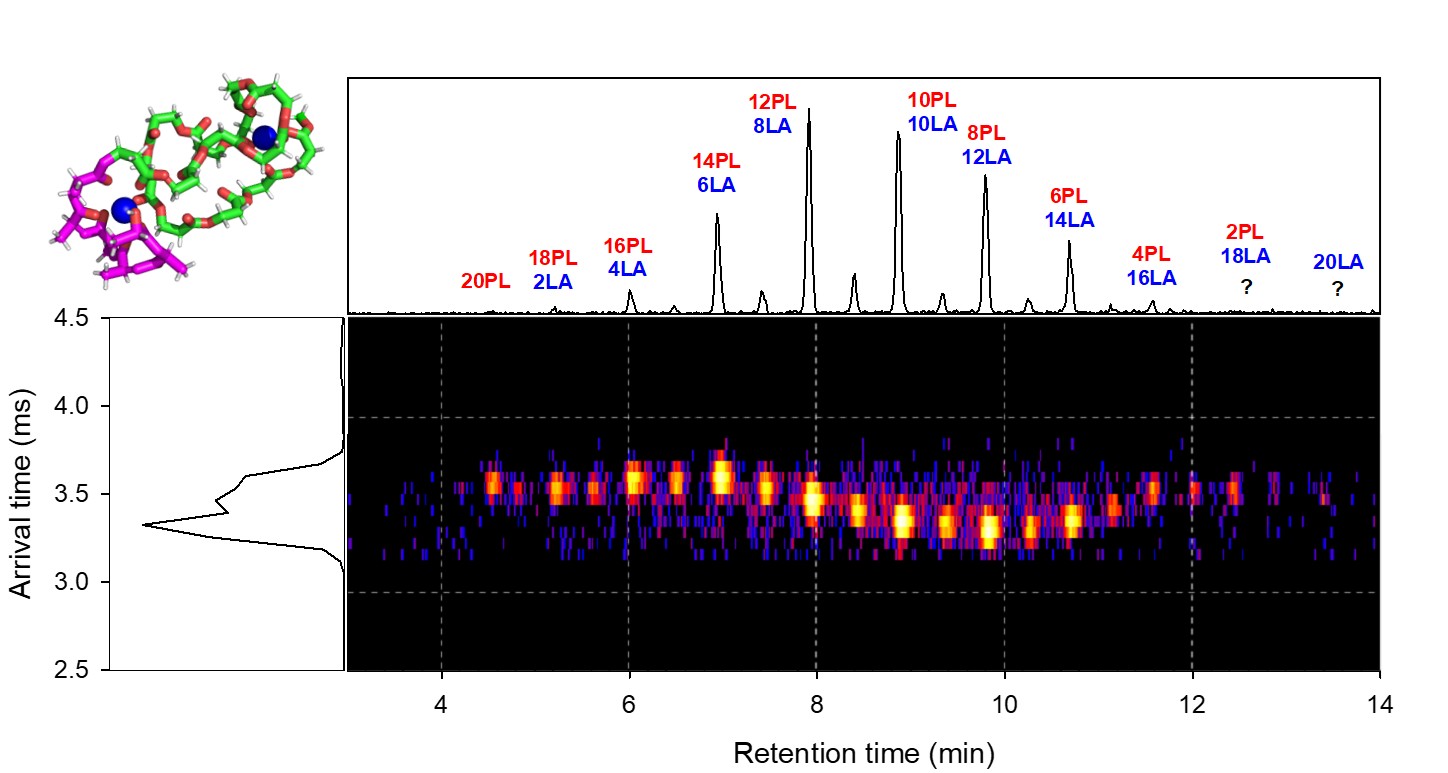
In this work, we evaluate whether a relationship exists between the primary structures of synthetic homo and copolymers and their secondary structures as gaseous ions. IMS−MS experiments are further complemented by MD simulations. To highlight the effectiveness of IMS separation, we selected isomeric homo and copolymers made of lactide (LA) and propiolactone (PL) units. In this way, the mass analysis becomes useless since isomeric comonomer sequences can coexist for any given chain length. An UPLC method is implemented in the workflow to successfully separate all PL−LA comonomer sequences before infusion in the IMS−MS instrument. The analysis of doubly charged copolymers shows that the comonomer sequence has an impact on the IMS response. However, this only holds for copolymer ions with precise sizes and charge states, and this is therefore not a rule of thumb.