Horse Chestnut Saponins–Escins, Isoescins, Transescins, and Desacylescins
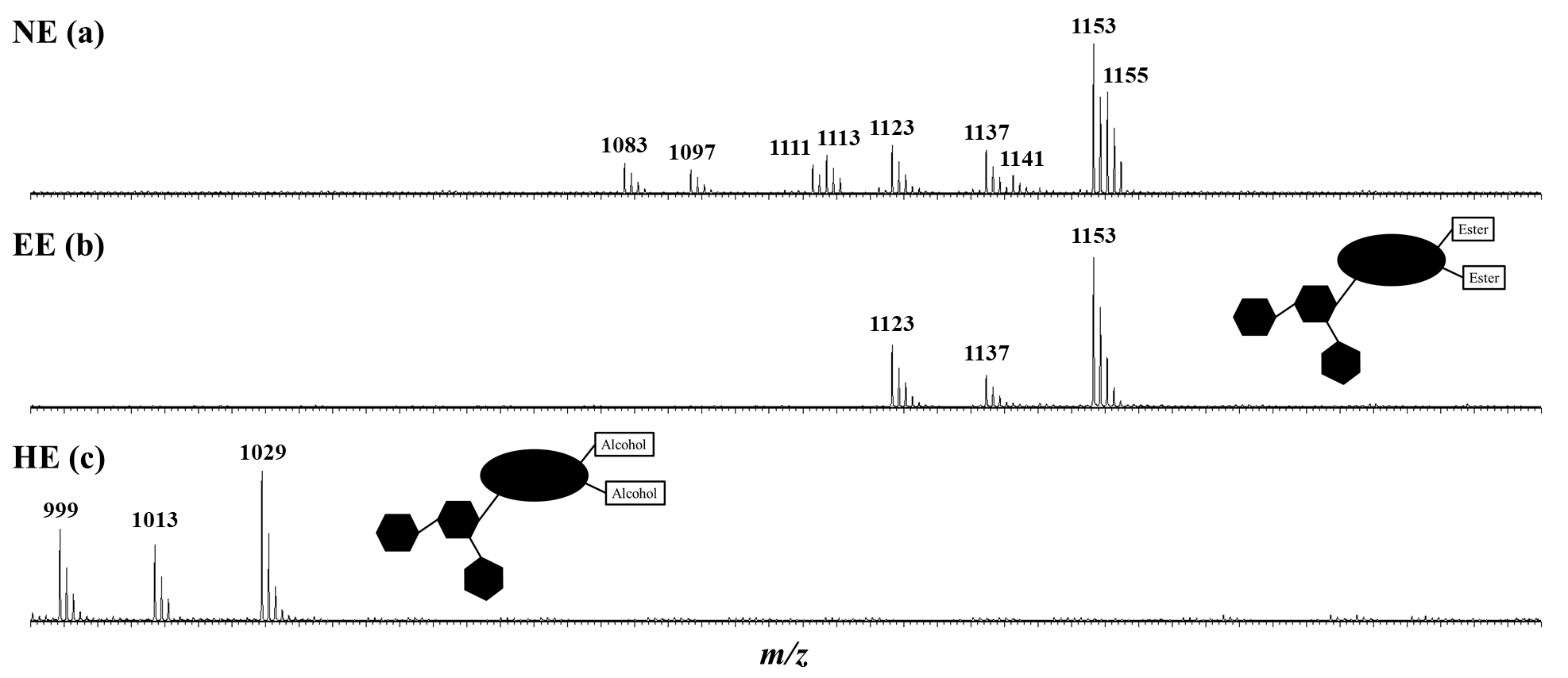
Escins constitute an abundant family of saponins (saponosides) and are the most active components in Aesculum hippocastanum (horse chestnut—HC) seeds. They are of great pharmaceutical interest as a short-term treatment for venous insufficiency. Numerous escin congeners (slightly different compositions), as well as numerous regio-and stereo-isomers, are extractable from HC seeds, making quality control trials mandatory, especially since the structure–activity relationship (SAR) of the escin molecules remains poorly described. In the present study, mass spectrometry, microwave activation, and hemolytic activity assays were used to characterize escin extracts (including a complete quantitative description of the escin congeners and isomers), modify the natural saponins (hydrolysis and transesterification) and measure their cytotoxicity (natural vs. modified escins). The aglycone ester groups characterizing the escin isomers were targeted. A complete quantitative analysis, isomer per isomer, of the weight content in the saponin extracts as well as in the seed dry powder is reported for the first time. An impressive 13% in weight of escins in the dry seeds was measured, confirming that the HC escins must be absolutely considered for high-added value applications, provided that their SAR is established. One of the objectives of this study was to contribute to this development by demonstrating that the aglycone ester functions are mandatory for the toxicity of the escin derivative, and that the cytotoxicity also depends on the relative position of the ester functions on the aglycone.